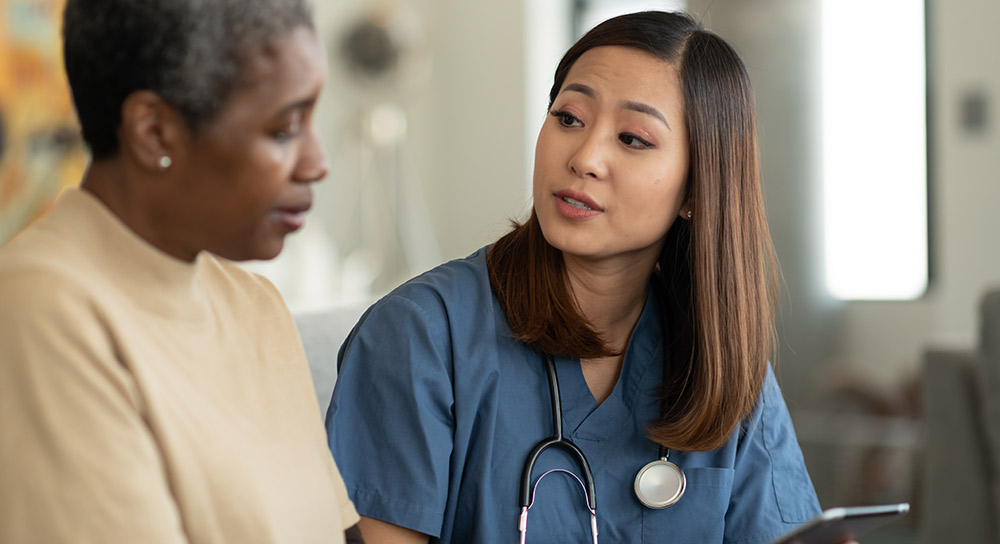
Heart disease is the number one cause of death in the U.S., according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). For people with diabetes, a chronic condition where their bodies can’t produce enough insulin, the risk of heart disease can double.
That’s a huge concern in the Central Valley where, as described by Dr. Manminder Bhullar, interventional cardiologist with Community Medical Centers, there’s a “diabetes epidemic.”
“Thirty to 40% of adults in the Central Valley have either prediabetes or diabetes,” Dr. Bhullar said.
Diabetes puts you at risk of heart disease
There are three main types of diabetes, and all of them can increase a patient’s risk of heart disease.
“Type 1 diabetes is usually hereditary, where people are born with it. The cardiovascular risk in Type 1 is equal as it is with Type 2, which is usually lifestyle changes along with some hereditary predisposition to develop diabetes. So, mainly the risk depends upon the duration of diabetes and how well the diabetes is controlled,” Dr. Bhullar explained.
“Gestational diabetes is a different subset. This is diabetes where high blood sugar is first detected during pregnancy and it almost affects 9% of pregnancies in the USA. These patients are at risk for developing diabetes or prediabetes later on in their life,” he added.
Some symptoms of diabetes
frequent urination
extreme fatigue
extreme thirst
But many patients have no symptoms at all or, if they do, they think they’re “just thirsty” or “just tired.” That can be a dangerous, and even deadly, oversight.
“Sometimes patients drink juice when they get too thirsty, and that can raise the blood sugar even higher and it can dehydrate them pretty fast. They can actually go into a state we call diabetic coma,” explained Dr. Varsha Babu, endocrinologist with Community Medical Centers.
According to the CDC, high blood sugar can damage vessels and nerves over time and impact the heart’s health.
“If you’re overweight and not exercising well it can cause plaque formation in the arteries supplying the heart and so these plaques can get bigger and bigger and completely cut down the circulation,” Dr. Babu explained.
“And can also affect the muscles of the heart. So the heart muscles get stiff so as per studies there has been increased risk of congestive heart failure,” she added.
Using state-of-the-art technology to monitor heart health
“We have various types of tests that are available to us, starting with basic tests like an echocardiogram, which is just an ultrasound of the heart. It detects your heart function,” said Dr. Bhullar.
“Then based on the patient’s symptoms, we have other tests like a non-invasive stress test that can help us detect any significant blockages in the heart blood vessels, and if necessary, we have an invasive procedure called an angiogram or left heart catheterization, where we inject dye directly into the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart and look for blockages.”
Protecting your heart
Regular physical activity and eating a well-balanced diet will also help regulate blood sugar levels and protect your heart.
Resources for learning about diabetes
If you are an adult living with diabetes, it is possible to effectively manage your condition, and live a long and healthy life. Visit our Diabetes Education Center to learn more.
See this story on MedWatch Today